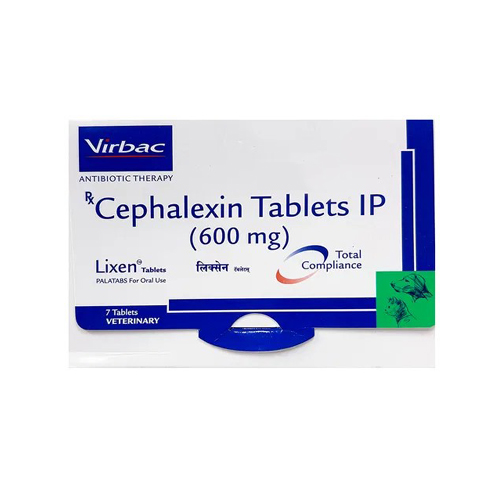
Complete Guide to Ecotas Bolus for Horses: Probiotics, Prebiotics & Growth Support Explained
Horses, like humans, rely heavily on a healthy gut for overall wellness and performance. In today’s intensive equine practices, horses are often subjected to stress, antibiotics, feed changes, and environmental variations—all of which can disrupt the balance of their gut microbiota. Formulated specifically for equines, it aids digestion, supports immunity, and promotes optimal growth and vitality.
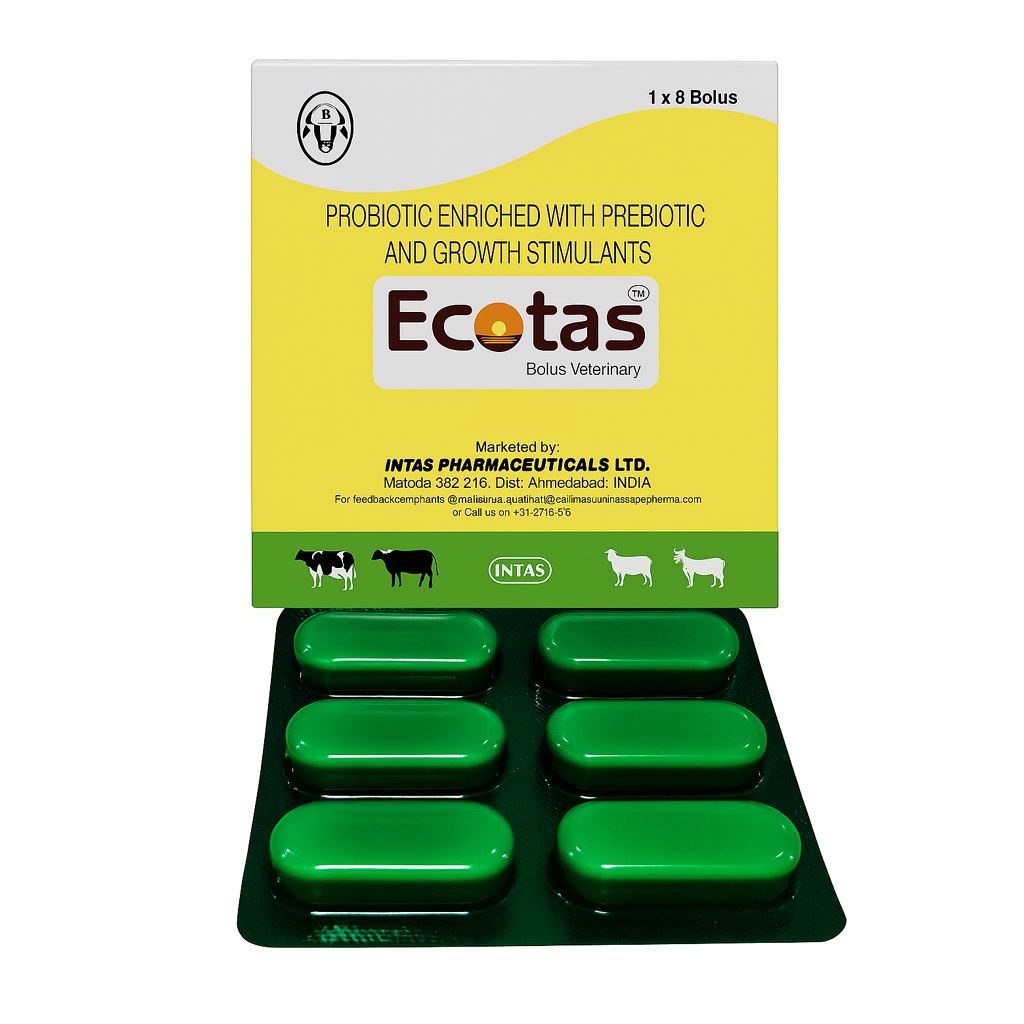
What Is Ecotas Bolus for Horses?
Ecotas Bolus is a veterinary-grade nutritional supplement designed to improve gut health and overall performance in horses. It combines probiotics, prebiotics, and growth stimulants to restore the natural balance of intestinal flora and boost immunity, especially after disease, antibiotic therapy, or digestive disturbances.
Key Components:
- Probiotics:
Live beneficial microorganisms that help maintain a healthy microbial balance in the digestive tract. - Prebiotics:
Non-digestible fibers that feed and promote the growth of probiotics in the gut. - Growth Stimulants:
Natural ingredients that enhance metabolic activity and support growth and energy utilization.
Why Gut Health Matters in Horses
The equine digestive system is uniquely complex, especially the hindgut, which houses billions of microorganisms crucial for breaking down fibrous food. When this system is compromised, it can lead to:
- Colic
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Poor performance
- Behavioral issues
Ecotas Bolus helps prevent these issues by promoting a healthy gut environment and nutrient absorption.
Indications for Use of Ecotas Bolus in Horses
Ecotas Bolus is widely used across various equine scenarios. Below are the key clinical and supportive indications:
1. After Antibiotic or Anthelmintic Treatment
- Antibiotics kill both harmful and beneficial bacteria.
- Ecotas Bolus helps replenish gut flora to prevent dysbiosis.
2. Stressful Conditions
- Travel, competition, training, and climate changes cause stress.
- Stress disrupts gut microbiota; Ecotas restores balance.
3. Digestive Disorders
- Used in cases of diarrhea, constipation, bloating, and indigestion.
- Enhances fermentation and improves motility.
4. Post-Surgical Recovery
- Boosts immunity and accelerates convalescence.
- Helps regain appetite and nutritional absorption.
5. Malnutrition or Poor Growth
- Delivers growth stimulants for weight gain and muscle mass.
- Promotes healthy metabolism and feed efficiency.
6. Foals with Weak Immunity
- Supports immune development and resistance to pathogens.
- Prevents neonatal diarrhea and failure to thrive.
7. Performance Enhancement in Sport Horses
- Improves stamina and digestion during heavy workloads.
- Helps maintain body condition and energy levels.
Dosage and Administration of Ecotas Bolus for Horses
Administering the correct dosage of Ecotas Bolus is crucial to ensure its effectiveness in promoting digestive health, improving immunity, and enhancing overall performance in horses.
General Guidelines
- Route of Administration: Oral
- Form: Bolus (tablet form)
- Frequency: Once or twice daily, as per veterinary direction
- Method: Can be administered using a balling gun, or crushed and mixed with molasses, bran mash, or feed if needed for palatability.
Dosage
| Horse Category | Body Weight | Recommended Dosage | Duration |
| Adult Horse (Maintenance) | 400–600 kg | 1 bolus once daily | 5–7 days |
| Adult Horse (Therapeutic) | 400–600 kg | 1 bolus twice daily | 5–10 days or as prescribed |
| Foals (Below 200 kg) | Under 6 months | ½ bolus once or twice daily | 3–5 days |
| Post-Antibiotic Recovery | Any weight | 1 bolus once daily | 7–10 days |
| Stress/Performance Horses | Any weight | 1 bolus daily during high workload | 7–14 days or longer if advised |
| Chronic GI Conditions | Any weight | 1 bolus twice daily | Until improvement is observed |
Administration Tips
- Use a Balling Gun:
- Hold the horse’s head up gently.
- Place the bolus deep in the back of the tongue using a balling gun.
- Crush & Mix (For Picky Eaters):
- Crush the bolus and mix with feed, honey, or molasses.
- Ensure the horse finishes the entire portion to receive the full dose.
Important Considerations
- Do not administer more than the recommended dose unless prescribed by a veterinarian.
- Continue administration for the entire recommended course, even if signs of improvement appear early.
Veterinary Advice
Before beginning any supplementation, especially for horses with chronic illness, pregnancy, lactation, or post-surgical recovery, veterinary consultation is strongly advised to tailor the dosage precisely.
Benefits of Using Ecotas Bolus in Horses
Here’s a summary of the wide-ranging benefits:
Digestive Health
- Maintains microbial balance
- Enhances feed digestion and absorption
- Prevents indigestion and gas accumulation
Immune Support
- Promotes gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) function
- Increases resistance against infections
Improved Growth & Performance
- Stimulates healthy growth in young horses
- Enhances endurance and recovery in performance horses
Faster Recovery
- Supports healing after illness, surgery, or antibiotic use
Detoxification
- Helps in clearing toxins through gut flora modulation
Safety Precautions and Considerations for Ecotas Bolus for Horses
Safety Precautions
- Consult a Veterinarian First
- Always seek veterinary guidance before beginning supplementation, especially for horses with underlying health issues or pregnant/lactating mares.
- Follow Exact Dosage
- Do not exceed or underdose.
- Proper Administration Method
- Use a balling gun or mix crushed bolus with feed to ensure full intake.
- Monitor for Side Effects
- Though rare, watch for signs like bloating, loose stools, or allergic reactions. Discontinue use if adverse effects appear.
- Storage Guidelines
- Store in a cool, dry place below 30°C, away from moisture and sunlight to preserve probiotic viability.
- Clean Handling
- Wash hands before and after use; keep bolus in its packaging until use to avoid contamination.
- Use Only in Horses
- Not intended for other animals like dogs, cats, or cattle unless directed by a vet.
- Avoid Mixing with Similar Supplements
- Do not combine with other probiotic/prebiotic products unless advised by a vet to prevent overdosing or microbial imbalance.
Considerations and Possible Cons
- Not a Replacement for Medical Treatment
- Ecotas Bolus supports health but does not replace antibiotics, dewormers, or clinical therapies when needed.
- May Not Be Suitable for All Horses
- Horses with severe GI infections, metabolic disorders, or autoimmune conditions may need alternative treatments.
- Mild Digestive Upset Possible Initially
- Some horses may experience bloating or gas during the first 1–2 days of use as gut flora adjust.
- Requires Consistent Use
- Irregular dosing may reduce effectiveness; requires commitment to full course.
- Cost Factor
- High-quality boluses with probiotics and growth factors can be more expensive than basic supplements.
- Limited Research in Specific Conditions
- While generally beneficial, more clinical trials are needed for efficacy in certain chronic equine conditions.
Veterinary Endorsement
Veterinarians recommend Ecotas Bolus for its multi-functional support. It is a go-to supplement in:
- Rehabilitation centers
- Breeding farms
- Racing stables
- Equine hospitals
Veterinary Note:
“Ecotas Bolus is an excellent addition to equine recovery and performance regimens. It addresses both prevention and therapy through natural gut modulation.” — Dr. M. K. Verma, Equine Specialist
Scientific Research Supporting Ecotas Bolus for Horses
The formulation of Ecotas Bolus is based on peer-reviewed scientific evidence that highlights the critical role of probiotics, prebiotics, and natural growth stimulants in equine gut health and systemic immunity. Below is a summary of relevant research and studies that support the ingredients used in Ecotas Bolus.
1. Probiotics in Equine Gastrointestinal Health
They are commonly used in equine nutrition to enhance microbial balance in the gut.
Research Highlights:
- Weese et al. (2004) found that Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species improve microbial diversity in horses’ colons, especially following antibiotic treatments.
- Yuyama et al. (2002) observed improved nutrient absorption and stool quality in horses supplemented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- A study published in the Journal of Equine Veterinary Science (2013) showed that horses receiving probiotics demonstrated fewer episodes of diarrhea during periods of stress and transport.
Conclusion: Probiotics support microbial balance, prevent gastrointestinal disturbances, and enhance immune function in horses.
2. Growth Stimulants and Feed Efficiency
Growth stimulants in veterinary supplements refer to natural compounds that enhance nutrient utilization, metabolism, and body weight gain, especially in young or recovering animals.
Research Highlights:
- A study by Kaneene and Hurd (2004) showed that horses receiving supplements with digestive enhancers and immune modulators experienced better feed conversion ratios and weight gain.
- Kirkland et al. (2005) demonstrated increased muscle tone and body condition in foals given yeast-based probiotic blends with trace growth-supporting nutrients.
Conclusion: Nutritional growth stimulants combined with gut modulators support improved growth and recovery, especially in foals, elderly, or stressed horses.
3. Ecotas Bolus-Type Formulas in Veterinary Practice
Although specific branded studies for Ecotas Bolus may be limited, its ingredients are widely studied in veterinary medicine. Formulas combining Lactobacillus spp., Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and MOS have been shown to:
- Strengthen mucosal immunity
- Reduce post-antibiotic complications
- Enhance nutrient absorption and weight gain
Veterinary Note:
“Gut health is the cornerstone of equine performance. Synbiotic supplements like Ecotas Bolus can drastically reduce the need for aggressive treatments later by building resilience early.” — Dr. L. C. Thomas, DVM, Equine Internal Medicine
Conclusion
Ecotas Bolus for Horses is not just a probiotic—it’s a comprehensive equine health supplement designed to support digestion, immunity, recovery, and growth. With the power of probiotics, prebiotics, and growth stimulants, it addresses the full spectrum of gut-related health challenges in horses.Whether you’re managing a high-performance racehorse or nurturing a young foal, Ecotas Bolus is a proven solution to keep your horse at its healthiest. Make it a part of your regular equine care program and witness the difference in condition, behavior, and performance. By combining the power of beneficial microorganisms with prebiotic fibers and growth-enhancing agents, Ecotas Bolus helps restore microbial balance, prevent gastrointestinal disturbances, and improve feed conversion.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.